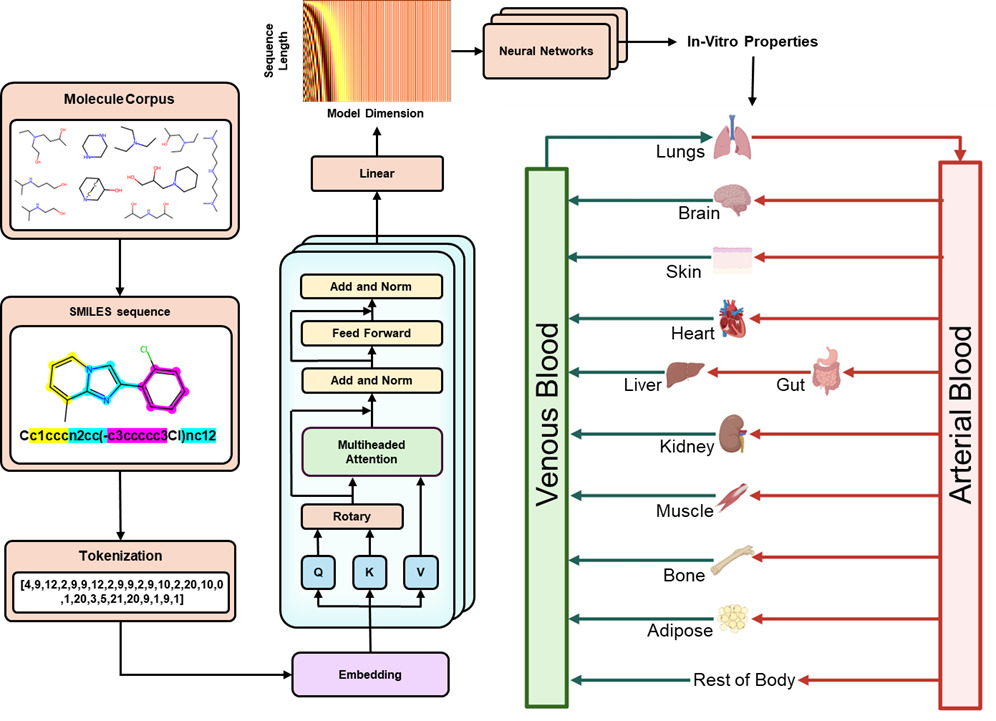
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models are widely used for mechanistic drug disposition studies, but they require experimentally measured parameters, which limits large-scale early-stage screening. This project integrates transformer-based pharmacokinetic property predictions with PBPK modeling to reduce dependence on experimental testing.
Key contributions:
- Transformer-predicted pharmacokinetic parameters, including intrinsic clearance, renal clearance, plasma protein binding, and permeability.
- Integration with PBPK models, allowing for rapid in silico pharmacokinetic assessments while maintaining mechanistic interpretability.
- Scalable and efficient screening, reducing the time and cost of drug candidate evaluation.
By combining data-driven property prediction with PBPK modeling, this hybrid framework provides a faster and more scalable approach to pharmacokinetic assessments in drug discovery.