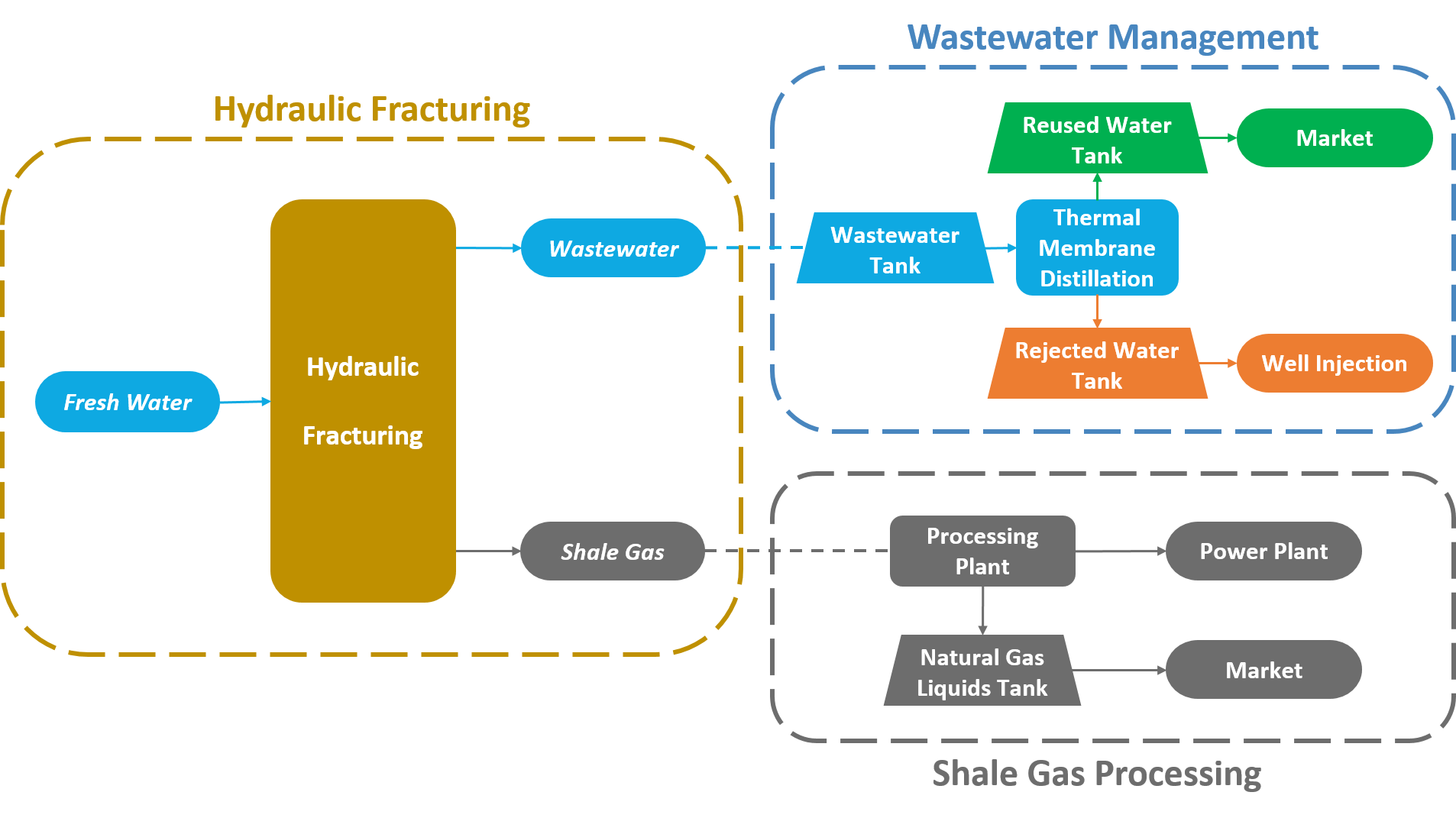
 The entire superstructure of shale gas development can be divided into the following three sub-processes: 1) hydraulic fracturing; 2) wastewater management; and 3) shale gas processing. Currently, these three sub-processes are studied independently without considering their interactions. However, it is very important to understand the complex connections among these sub-processes as they are dependent on each other. In hydraulic fracturing, it is very important to create fractures with optimal propped fracture geometry as it will lead to maximum shale gas production. However, as hydraulic fracturing requires a huge amount of water resources, the profit generated by the extraction of shale gas accompanies environmental concerns, particularly many water-related issues. One of the important concerns is that a certain amount of the injected fracturing fluid flows back to the surface as wastewater, containing high concentrations of various contaminants. Thus, developing an environmentally sustainable and economically viable water management plan along with optimizing production is crucial for wastewater treatment and supplying sufficient freshwater to drilling sites. Furthermore, since shale gas is a hydrocarbon mixture mainly consisting of methane, it requires additional processing units for its subsequent use. Motivated by these
The entire superstructure of shale gas development can be divided into the following three sub-processes: 1) hydraulic fracturing; 2) wastewater management; and 3) shale gas processing. Currently, these three sub-processes are studied independently without considering their interactions. However, it is very important to understand the complex connections among these sub-processes as they are dependent on each other. In hydraulic fracturing, it is very important to create fractures with optimal propped fracture geometry as it will lead to maximum shale gas production. However, as hydraulic fracturing requires a huge amount of water resources, the profit generated by the extraction of shale gas accompanies environmental concerns, particularly many water-related issues. One of the important concerns is that a certain amount of the injected fracturing fluid flows back to the surface as wastewater, containing high concentrations of various contaminants. Thus, developing an environmentally sustainable and economically viable water management plan along with optimizing production is crucial for wastewater treatment and supplying sufficient freshwater to drilling sites. Furthermore, since shale gas is a hydrocarbon mixture mainly consisting of methane, it requires additional processing units for its subsequent use. Motivated by these
considerations, we focus on the development of a novel framework that integrates hydraulic fracturing, wastewater generation and management, and shale gas production and management to achieve a sophisticated understanding of the complex connections between these sub-processes and to optimize the superstructure of shale gas development.
Literature:
K. Cao, P. Siddhamshetty, Y. Ahn, R. Mukherjee, and J. S. Kwon, “Economic model-based controller design framework for hydraulic fracturing to optimize shale gas production and water usage”, Ind. & Eng. Chem.Res., 2019, 58, 12097-12115.
Y. Ahn, P. Siddhamshetty, K. Cao and J. S. Kwon, “Optimal design of shale gas supply chain network considering MPC-based pumping schedule of hydraulic fracturing in unconventional reservoirs,” Chem. Eng. Res. & Des., 2019, 174, 412-429.
P. Etoughe, P. Siddhamshetty, K. Cao, R. Mukherjee, and J. S. Kwon, “Incorporation of sustainability in process control of hydraulic fracturing in unconventional reservoirs,” Chem. Eng. Res. & Des., 2018, 139, 62-76.