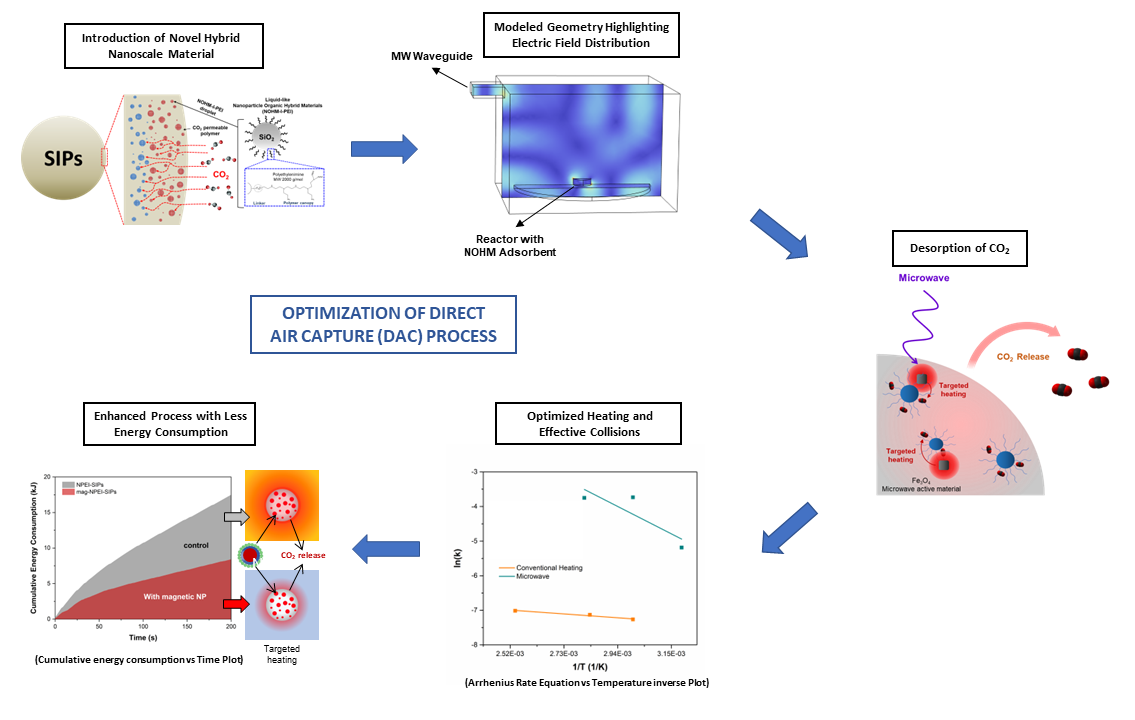
Direct Air Capture (DAC) process involves adsorption of CO2 and subsequently, the prime task is to get rid of the adsorbed CO2, through the process of regeneration that is achieved by heating. In our group, we simulate the system of the adsorbent during the regeneration process to study the spatiotemporal distribution of the temperature inside the Hybrid Nanoscale Multifunctional Material that has been designed with special properties to achieve the optimal targeted heating, under the subjugation of microwave. The key motive of this high-fidelity model is to deal with the optimization of the adsorbent material design, designating the combination of parameters that result in the novelty of the adsorbent material. The overall methodology saves the total energy consumption in the process of regeneration, hence making the DAC process more sustainable and cost-effective, which holds immense value as there is a dire need to achieve the net-zero targets by the year 2050.
Literature: